
RGB and CMYK: Understanding color models used in design
Different devices use diverse color methods. Two color models are usually used in design, RGB and CMYK.
RGB stands for the three additive primary color, Red, Green, and Blue. It is used for anything, that is displayed in electronic systems, on monitors, televisions, but it is used in conventional photography, as well.
Web design is built on the RGB color method. On the screen there are millions of pixels, and each pixel consists of three subpixels, red, green and blue. It is an additive color model. The broad array of colors of your screen is an addition of red, green and blue light. As you display them on a white screen, where they lap over, you can see the secondary colors. The equal combination of red, green and blue light at full intensity makes white, zero intensity for each three color light creates black. When the concentrations of red, green and blue light are the same, it gives a tone of gray, depending on their intensity of how light or dark the gray is. When they are different, then you create a color hue. The saturation depends on the difference between the strongest and weakest intensity of the primary colors. When one of the three colors has the strongest intensity, it is similar to the pure hue of the primary color. When two of the components have the same strong intensity, the hue of a secondary color is created. E.g., when you have the equal intensity of red and green, and zero blue, you have yellow. Cyan is created by green and blue at the same intensity, and magenta by red and blue.
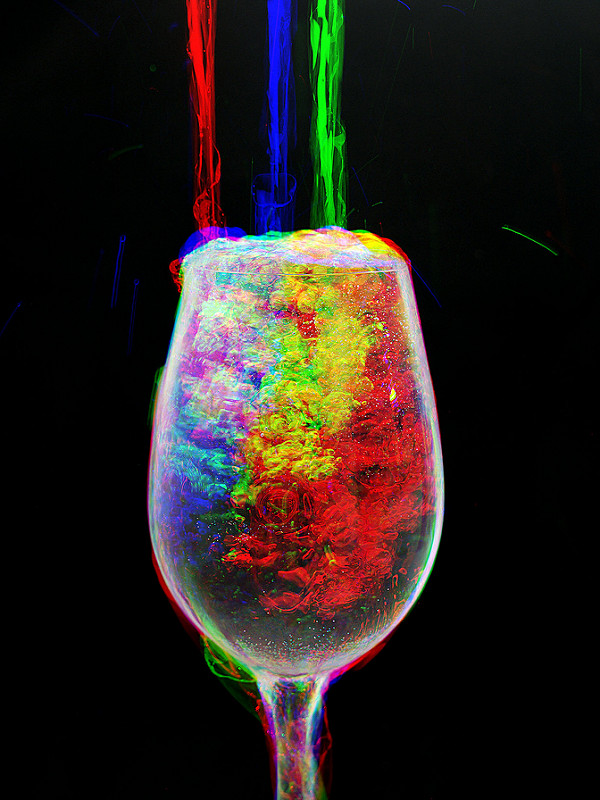
In this color model, colors are determined by a hex code. Each three primary color can have 256 shades, which means altogether is 16,7 million different shades, tints, and tones that we can choose from. Colors are settled in hexadecimal scale. It uses sixteen different symbols, 0–9 to represent values from zero to nine, and A–F to represent values ten to fifteen. It means that regarding each primary color, from two characters you will get the 256 shades. 0 is the darkest shade, F is the lightest tint. As we have 3 primary colors, the hex code for black looks like this: #000000, while the hex code for white is: #FFFFFF. The hex code for red is: #FF0000, for green it is: #00FF00 and for blue is: #0000FF. By knowing all this, you can create the hex code for yellow: #FFFF00. Of course, you can play with the codes to create millions of different shades, tones, and tints. Do not worry; you do not need to know all these codes by heart. You can see the hex codes in all the graphical programs, also if you are interested in more details, on the internet there are tones of information on the topic.
In web design you work in RGB color model; however, it is good to know that on the other hand e.g. color printers do not use this additive color method, but they are subtractive color devices, most of them based on the CMYK color model.
CMYK represents the four inks used during printing, Cian, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (blacK). This color model is applied to paints, inks, dyes, all other stuff whose color depends on the reflecting light under we see them. The ink absorbs the light. This is why the model is called a subtractive model. The ink “subtracts” red, green and blue from the light. If red is absorbed from white light, there is cyan left, if green is subtracted, then you get magenta, and if blue is left out, the result is yellow. All colors are dissociated for cyan, magenta, yellow and black. The image that we print out consists of tiny dots with these four colors. The bigger the dot, the more the color is represented.
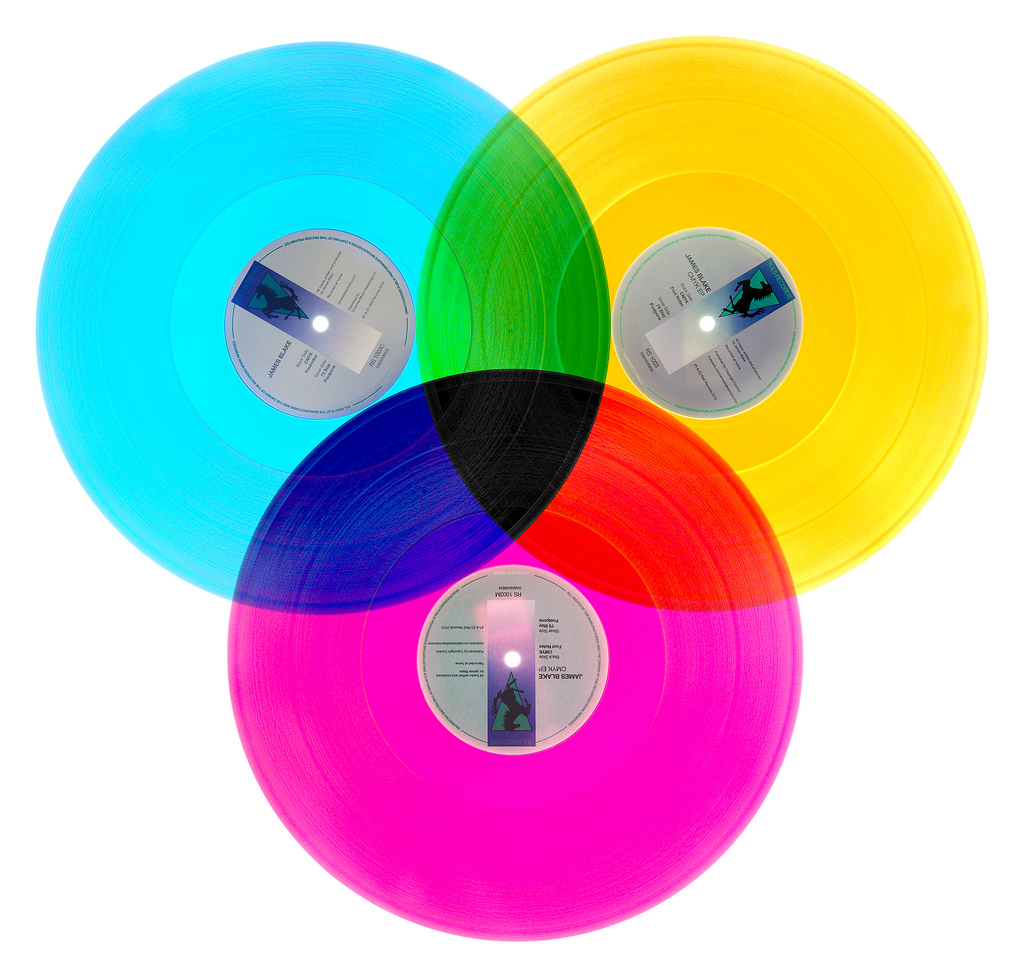
As I have already mentioned above, when we mix equally the three primary color lights in the additive RGB color model, we create white, while black is the absence of light. On the contrary, when we mix cyan, magenta and yellow in CMYK, we get black, and white is usually the color of paper we print on. To get deeper black shades, and to save the cost, of course, typically black ink is used, as well.
To summarize it quickly, what goes into your computer through scanner, or camera it is in RGB, but what comes out of it via printing is in CMYK. This is why you might see a different picture on your monitor and when you print it out. You have to be aware that you need four times better capacity printer to get about the same quality in printing than on your monitor.
Reference:
- Video: Express Cards: What is the difference between RGB and CMYK?
- Online Webdesign Tanfolyam – A színelmélet alapjai
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RGB_color_model
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CMYK_color_model
Recommended posts
Understanding Color Terminology
Understanding Color Terminology Using colors in your design is essential, and if you would like to do it expertly, firstly you need to know some basic concepts in color theory. For creating fabulous color schemes, you have to use the thesaurus of the hues, their...
read moreColor Harmonies
Color Harmonies In my previous article, "The Meaning of Colors" we discussed the exciting world of colors, we understood that using a wide range of shades, tones, and tints of the same hues, can evoke different feelings, that is why it is vital to always use the...
read moreThe Meaning of Colors
The Meaning of Colors "Color creates, enhances, changes, reveals and establishes the mood of the painting.” Kiff Holland perfectly enhances the importance of colors, not just in paintings and fine art, but everywhere in our life we are surrounded by them and under the...
read more


